P331 - Verify Preorder Serialization of a Binary Tree
Problem Abstract
Given a binary tree, serialize it using preorder traversal:
- a non-null node, record the node's value,
- a null-node, record a sentinel value such as '#'.
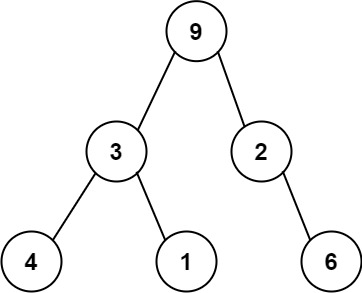
For example, using 9,3,4,#,#,1,#,#,2,#,6,#,# represents the following tree.
Solution
Simulation of re-constructing the tree
rust
/// runs in O(n)/O(n)
pub fn is_valid_serialization(preorder: String) -> bool {
let mut bytes = preorder.split(",");
preorder_traverse(&mut bytes) && bytes.next().is_none()
}
fn preorder_traverse<'a>(bytes: &mut Split<'a, &str>) -> bool {
if let Some(s) = bytes.next() {
// it's a sentinel value
if s == "#" {
return true;
}
if !preorder_traverse(bytes) {
return false;
}
if !preorder_traverse(bytes) {
return false;
}
return true;
}
false
}Consider the quantity relationship between parent node and children nodes
A non-null node has two children, whatsever its two non-null children, or a null child and a non-null child, or two null children.
rust
/// runs in O(n)/O(n)
pub fn is_valid_serialization2(preorder: String) -> bool {
let bytes = preorder.as_bytes();
let n = bytes.len();
let mut stk = vec![1]; // there are only one root node
let mut i = 0;
while i < n {
// invalid situation encountered
if stk.is_empty() {
return false;
}
if bytes[i] == b',' {
i += 1; // skip
} else if bytes[i] == b'#' {
// a null child
*stk.last_mut().unwrap() -= 1;
if *stk.last().unwrap() == 0 {
stk.pop();
}
i += 1;
} else {
// It's a number
// read a number
while i < n && bytes[i] != b',' {
i += 1;
}
*stk.last_mut().unwrap() -= 1;
if *stk.last().unwrap() == 0 {
stk.pop();
}
stk.push(2); // a non-null node has two children
}
}
stk.is_empty()
}We could optimize it using just one counter.
rust
/// runs in O(n)/O(1)
pub fn is_valid_serialization3(preorder: String) -> bool {
let bytes = preorder.as_bytes();
let n = bytes.len();
let mut slots = 1;
let mut i = 0;
while i < n {
if slots == 0 {
return false;
}
if (bytes[i] == b',') {
i += 1;
} else if bytes[i] == b'#' {
slots -= 1;
i += 1;
} else {
// read a number
while i < n && bytes[i] != b',' {
i += 1;
}
slots += 1;
}
}
slots == 0
}